We are excited to announce the public availability of HashiCorp Vault 1.2. Vault is a tool to provide secrets management, data encryption, and identity management for any infrastructure and application.
Vault 1.2 is focused on supporting new architectures for automated credential and cryptographic key management at a global, highly-distributed scale. This release introduces new mechanisms for users and applications to manage sensitive data such as cryptographic keys and database accounts, and exposes new interfaces that improve Vault’s ability to automate secrets management, encryption as a service, and privileged access management.
- KMIP Server Secret Engine (Vault Enterprise only): Allow Vault to serve as a KMIP Server for automating secrets management and encryption as a service workflows with enterprise systems.
- Integrated Storage (tech preview): Manage Vault’s secure storage of persistent data without an external storage backend, supporting High Availability and Replication.
- Identity Tokens: Produce OIDC-compliant JWT tokens tied to Vault identities for use in third-party systems.
- Database Static Credential Rotation: Automate the rotation of pre-existing database credentials using the DB Secret Engine.
The release also includes additional new features, secure workflow enhancements, general improvements, and bug fixes. The Vault 1.2 changelog provides a full list of features, enhancements, and bug fixes.
»KMIP Server Secret Engine
Note: This is a Vault Enterprise feature
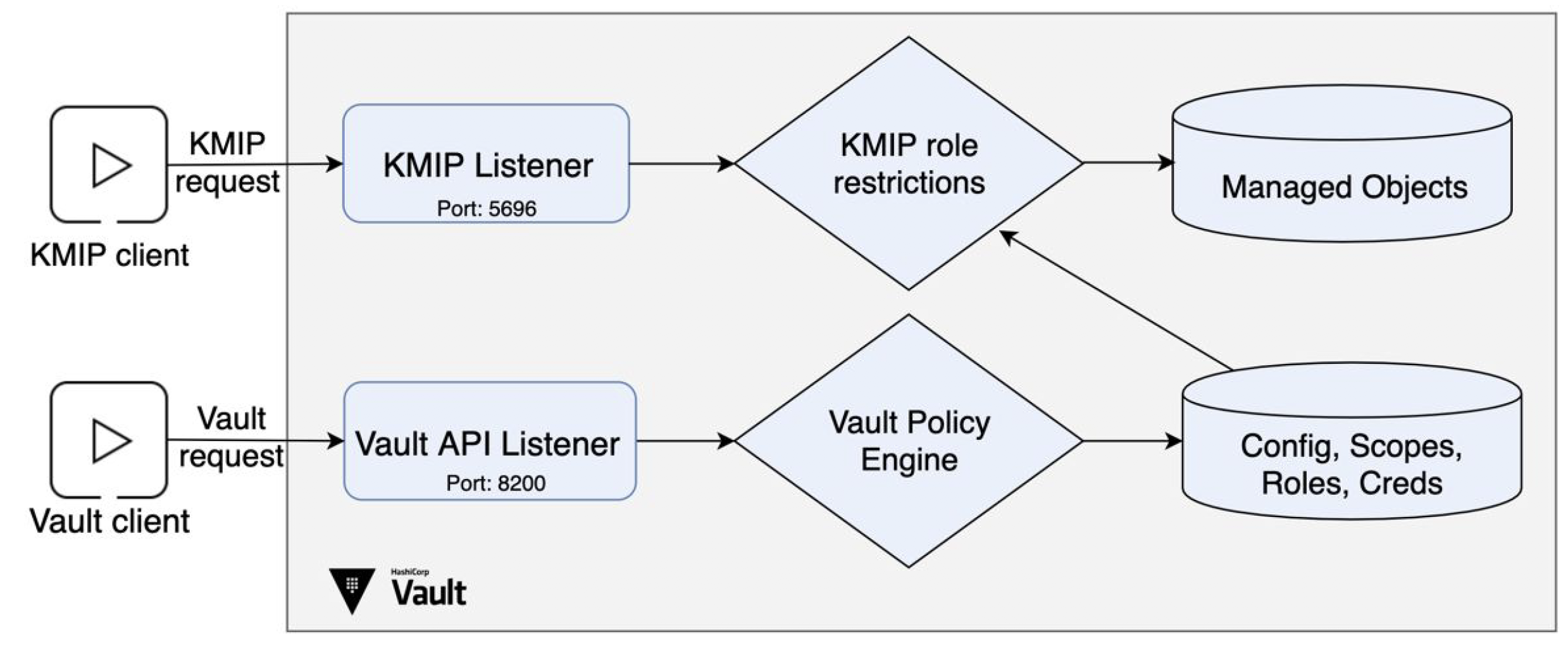
Vault Enterprise 1.2 sees the introduction of the Key Management Interoperability Protocol (or KMIP) standard as a new method for automatically integrating with many enterprise software and hardware platforms for secrets management.
KMIP is an open OASIS protocol for managing encryption workloads and data. KMIP instructions focus on tasks including key generation, key management, and encryption between a KMIP Client (an application or system requesting a cryptographic task) and a KMIP Server (a platform performing that cryptographic task).
In Vault Enterprise 1.2, we are introducing a new Secret Engine that supports Vault serving as a KMIP Server for client requests. This allows Vault to integrate with an ecosystem of over a hundred common enterprise platforms for use cases such as Transparent Database Encryption (TDE); Full Disk Encryption (FDE) and virtual volume encryption; and multi-cloud/hybrid cloud key Bring Your Own Key (“BYOK”) key management.
1.2 is the beginning of our story with supporting the KMIP protocol and not every instruction or object will be supported with this release. We will continue to support additional KMIP instructions and objects over the course of the next few releases, and are in the process of certifying Vault Enterprise interoperability with major enterprise infrastructure vendors. For more on Vault and KMIP, head over to Advanced Data Protection with Vault
Please consult our guide on the KMIP Secret Engine and documentation on KMIP for more information.
»Integrated Storage
Note: this is a preview release feature and Integrated Storage is currently not supported for production workloads in Vault Enterprise 1.2
Integrated Storage is a new feature in Vault 1.2 that allows Vault admins to configure an internal storage option for storing Vault’s persistent data at rest. Rather than using an external storage backend, Integrated Storage exists as a purely Vault internal option that leverages the Raft consensus protocol to provide highly available storage for Vault data. Our goal with integrated storage is to provide another option for managing Vault’s storage backend that doesn’t require proficiency in a separate tool or platform.
Integrated storage is being released as a tech preview feature, which means that we are not providing enterprise support for Vault Enterprise users deploying integrated storage in production in Vault 1.2. We’re excited to release this new architecture with the community to gather feedback, and will officially add it to our supported reference architecture for Vault Enterprise in a later release.
For more information on integrated storage, see here.
»Identity Tokens
Identity Tokens are OIDC compliant tokens that allow for third party applications to verify JWT-based claims on Vault identities. Using Identity Tokens, an application can verify a Vault entity, its group membership, and identity management system aliases without logging into Vault. Identity Tokens can also carry other metadata with them as desired that can be used for further identification/authorization uses..
For more information on Identity Tokens, see here.
»Database Static Credential Rotation
We have extended the database secret engine to now manage and rotate credentials for preexisting users in addition to Vault’s longstanding ability to generate a temporary set of full credentials including username. This allows Vault to securely serve as the source of truth for applications that utilize a series of “known” database logins and service traditional Privileged Access Management (PAM) use cases involving static DB credentials.
For more on the Database Secret Engine, see here.
»Other Features
There are many new features in Vault 1.2 that have been developed over the course of the 1.1.x releases. We have summarized a few of the larger features below, and as always consult the changelog for full details:
- Vault API explorer: The Vault UI now includes an embedded API explorer where you can browse the endpoints available to you and make requests. To try it out, open the Web CLI and type
api. - ElasticSearch database plugin: New ElasticSearch database plugin issues unique, short-lived ElasticSearch credentials.
- Pivotal Cloud Foundry plugin: New auth method using Pivotal Cloud Foundry certificates for Vault authentication.
- Vault Agent Namespace Support: Add optional
namespaceparameter, which sets the default namespace for the auto-auth functionality. - New UI Features: An HTTP Request Volume Page and new UI for editing LDAP Users and Groups have been added.
»Upgrade Details
Vault 1.2 introduces significant new functionality. As such, we provide both general upgrade instructions and a Vault 1.2-specific upgrade page.
As always, we recommend upgrading and testing this release in an isolated environment. If you experience any issues, please report them on the Vault GitHub issue tracker or post to the Vault mailing list.
For more information about HashiCorp Vault Enterprise, visit https://www.hashicorp.com/products/vault. Users can download the open source version of Vault at https://www.vaultproject.io.
We hope you enjoy Vault 1.2!