HashiCorp Vault 1.6 was released on November 11th, introducing some exciting new features and enhancements. Now you can visit the Vault 1.6 Release Highlights on HashiCorp Learn for our collection of new and updated tutorials for Vault 1.6.

Key Management Secrets Engine
As organizations adopt a cloud operating model, it is challenging to maintain centralized control over the generation and lifecycle of various keys while still being able to take advantage of native cloud integrations for securing data. Operating in multiple clouds can further amplify these challenges.
Vault 1.6 introduces a new Key Management Secrets Engine designed to help with cloud provider key lifecycle management.
NOTE: The Key Management Secrets Engine is a Technical Preview feature.
Vault GitHub Actions
Some GitHub repositories of web applications will require a Docker image, and that image requires the injection of secrets that you have stored in Vault. Currently, this process is accomplished either manually or through a continuous integration (CI) service. The process requires human intervention and sometimes fails to provide rich feedback alongside the GitHub repository.
The Vault GitHub Actions tutorial demonstrates the use of a GitHub workflow within your repository and requests the required secrets with Vault GitHub actions.
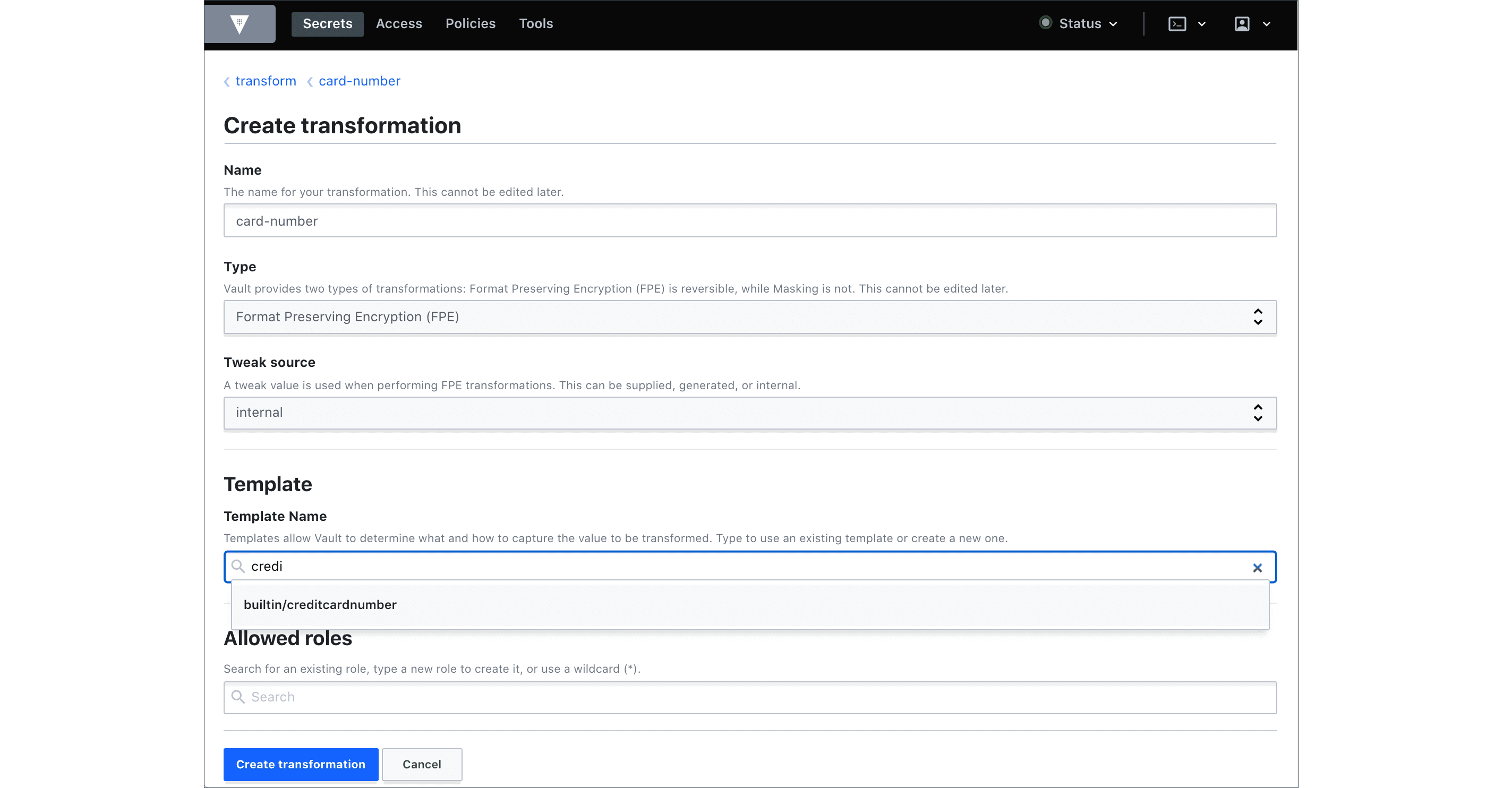
Tokenize Data with Transform Secrets Engine
The Tokenize Data with Transform Secrets Engine tutorial demonstrates a new data transformation method introduced in Vault 1.6. Tokenization transformation replaces sensitive data with unique values (tokens) that are unrelated to the original value in any algorithmic sense. Therefore, those tokens aren't at risk of being exposed in plaintext, thus satisfying PCI-DSS guidance.
NOTE: Tokenization transformation is available as a Technical Preview.

Transform Secrets Engine
Vault UI now supports the creation of transformations, roles, templates, and alphabets for the Transform secrets engine.
The Transform Secrets Engine tutorial was updated to demonstrate the new UI steps.
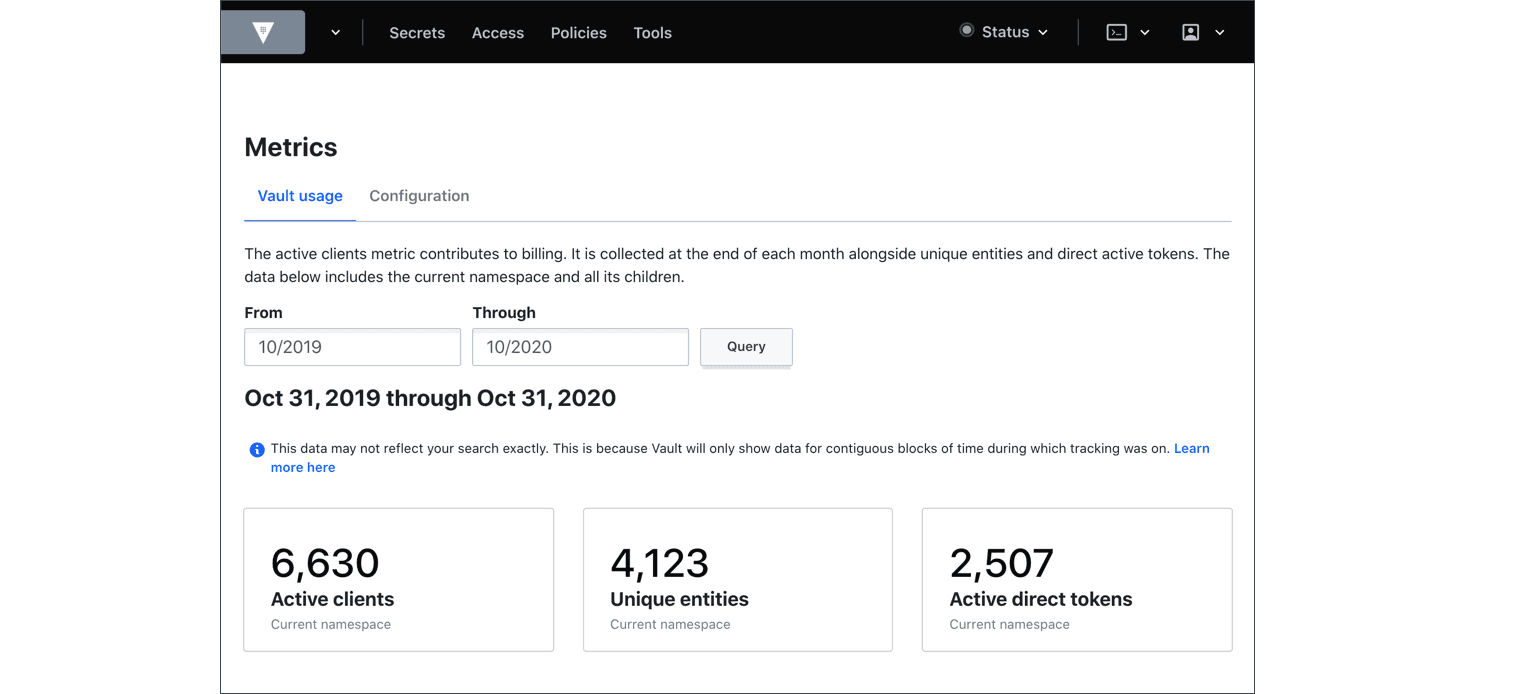
Vault Usage Metrics
The Vault Usage Metrics tutorial introduces the Vault Metrics dashboard in Web UI. Enhancements were made to Vault 1.6 to help discover active client count and historical client counts within Vault. Specifically, a new Vault usage command that can quickly reference client counts for an active system and tools for measuring client creation and historical client usage.
Integrated Storage New Features
Integrated Storage introduced cloud auto-join and automated snapshot features. Both the Vault HA Cluster with Integrated Storage and Vault HA Cluster with Integrated Storage on AWS tutorials were updated to demonstrate the data snapshot automation.
To learn about cloud auto-join, read the Vault HA Cluster with Integrated Storage on AWS tutorial.
Password Policies for Database Secrets Engine
Password policy was introduced in Vault 1.5, and Vault 1.6 extended its support to all databases in the Database Secrets Engine. The Dynamic Secrets: Database Secrets Engine tutorial was updated to demonstrate the use of password policy.
Codify Management of Vault Enterprise
The Codify Management of Vault Enterprise tutorial was updated to demonstrate an example of configuring Vault resources with nested namespaces.








